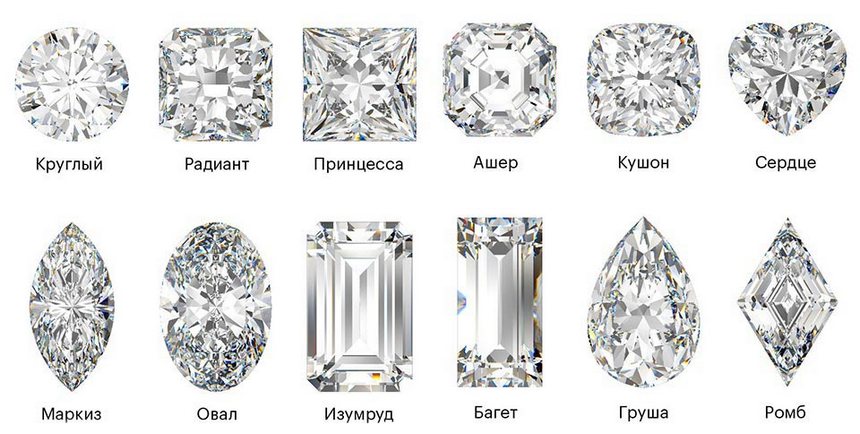
Classification of diamonds: mass, color, clarity

Diamonds are graded according to 4 main criteria, known as the “4Cs”: weight (carat), color, clarity and cut. Depending on these characteristics, diamonds are divided into different categories.
Weight of diamonds
The weight of diamonds is measured in units of carats. One carat is equal to 0.2 grams or 200 milligrams. A carat is divided into 100 “points,” which allows the weight of diamonds to be measured more accurately. For example, a 0.50 carat diamond can also be expressed as 50 points. Typically, diamonds are sold in weight categories such as 0.25 carat, 0.50 carat, 1 carat, etc. The weight of a diamond is one of the most important factors affecting its price and value.
Diamond diameter
The diameter of a diamond is also an important parameter that affects its appearance and price. The diameter of a diamond is measured in millimeters and is usually indicated in the description of the stone. The diameter of a diamond can vary depending on its weight and shape. For example, for round diamonds, the diameter can be determined by a formula that depends on the weight of the stone. For other diamond shapes (square, oval, emerald, etc.), the diameter can also be indicated in the description. The size of a diamond, combined with its weight and quality, determines its overall value and appeal.
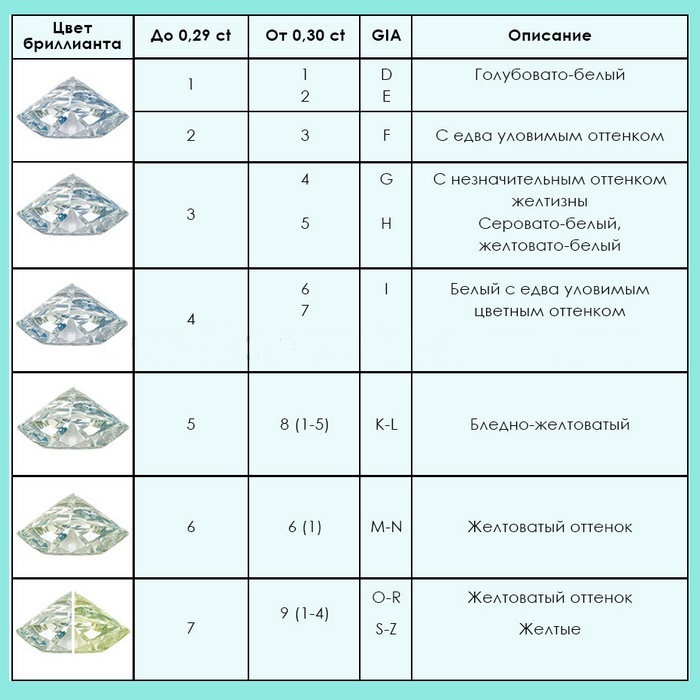
Diamond color
Diamonds are graded using the GIA (Gemological Institute of America) international scale, which includes 23 color levels, ranging from completely colorless (D) to visibly saturated (Z). The closer a diamond is to colorless (D), the higher its value. In practice, it is important to choose a diamond that appears colorless or has a faint color to make the stone appear brighter and shinier.
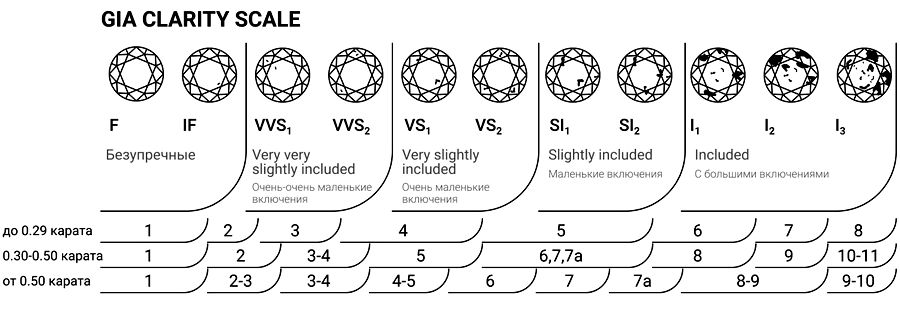
Diamond Clarity
Diamonds are graded using the GIA Clarity Score, which evaluates the presence of inclusions and blemishes within the stone. The fewer inclusions and defects, the cleaner and more valuable the diamond. The purest diamonds are considered Flawless and Internally Flawless, where there are no visible inclusions under 10x magnification. Diamonds with clarity ranging from VVS1 to VS2 (very, very small inclusions) are also considered to be of very high quality and have high value. Diamonds with clarity levels of SI1 to SI2 (small inclusions) and I1 to I3 (inclusions) are considered less pure and may be more affordable, but can still be beautiful and shiny.
Diamond cut
Diamond cutting is the process of treating and cutting a rough diamond to give it shape, symmetry and brilliance. Cut plays a key role in determining the beauty and value of a diamond, as it affects the stone's ability to reflect and refract light.
There are several different types of diamond cuts, each of which has its own characteristics and advantages: 











